BAU425 重庆生态谷城
中国,重庆市
科目
规划类型
城市规划及设计城市
中国,重庆市时间
2010名次
邀请竞赛业主
重庆市规划局项目
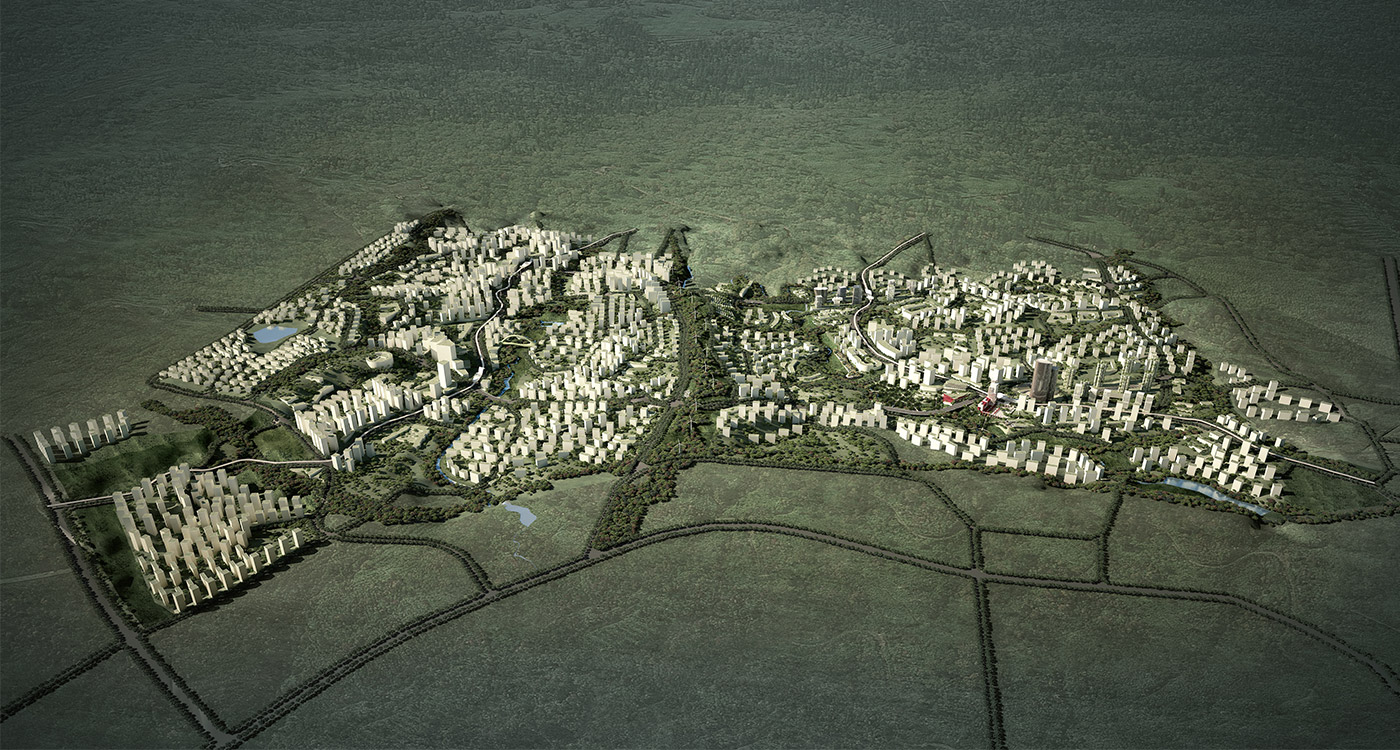
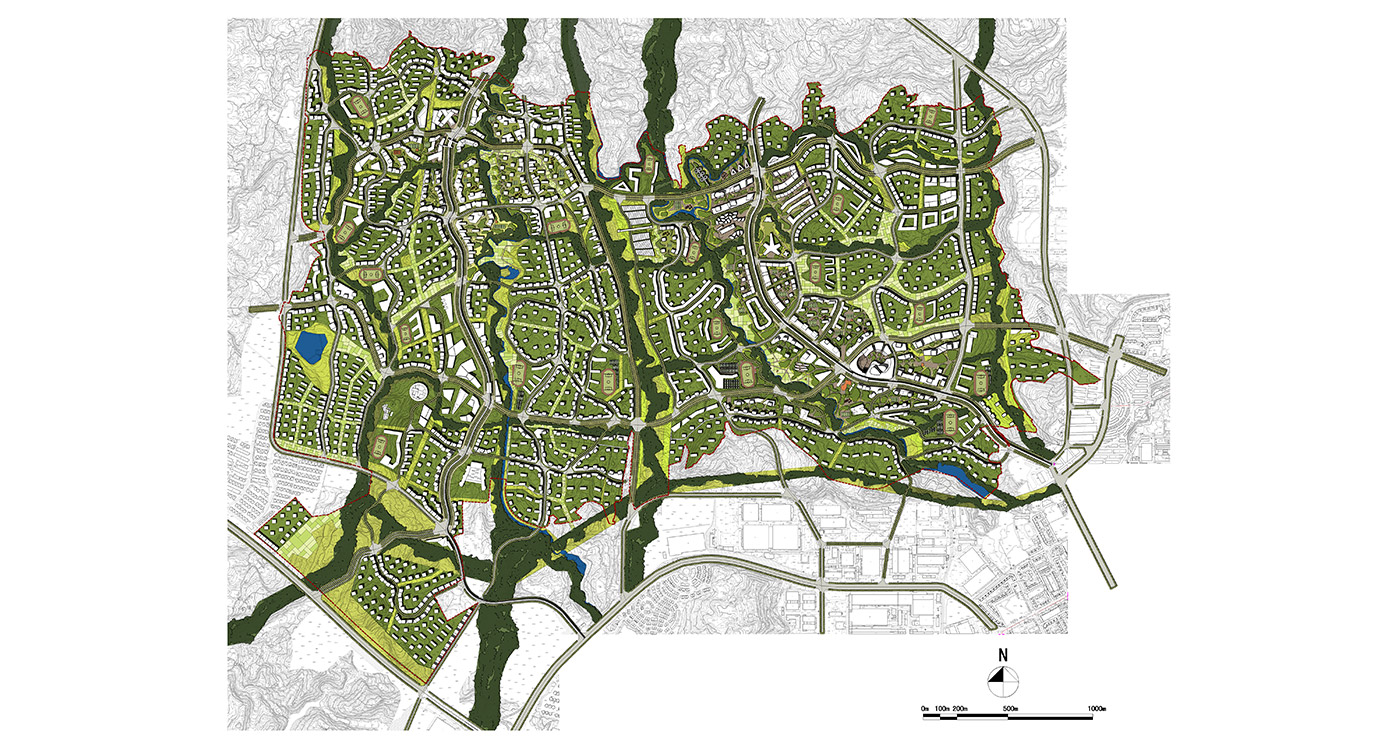
高密度绿色宜居生态谷eco urbanism
introduction
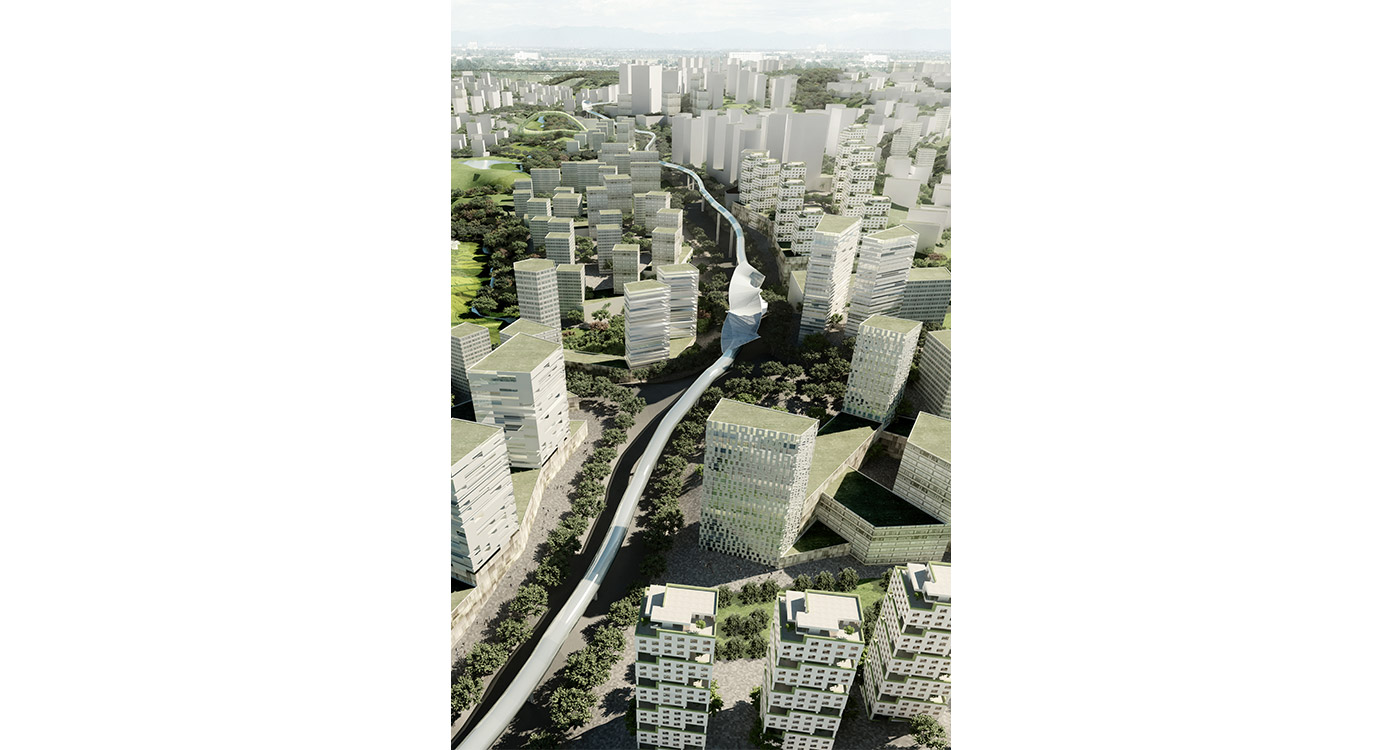
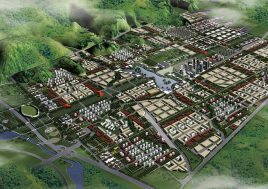
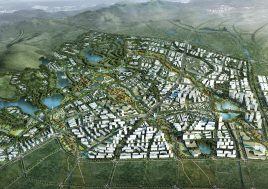
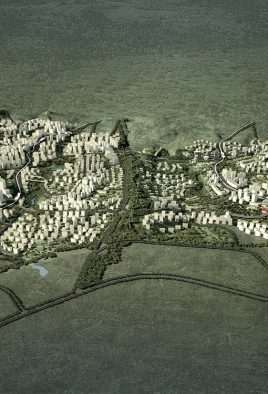
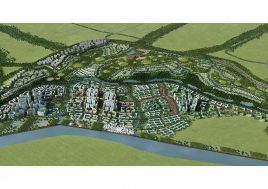
China is seeking to stimulate urban growth in its West provinces. This development zone is situated on the northern periphery of Chongqing, one of China’s megacities. Previously planned but not yet developed as an industrial district the site remains greenfield, with substantial existing vegetation, farming and some settlements with heritage value. The new postindustrial planning brief stipulates the area as an oversized residential cluster supporting the neighbouring hi-tech zone. It is mountainous and suffers from sweltering summer heat.
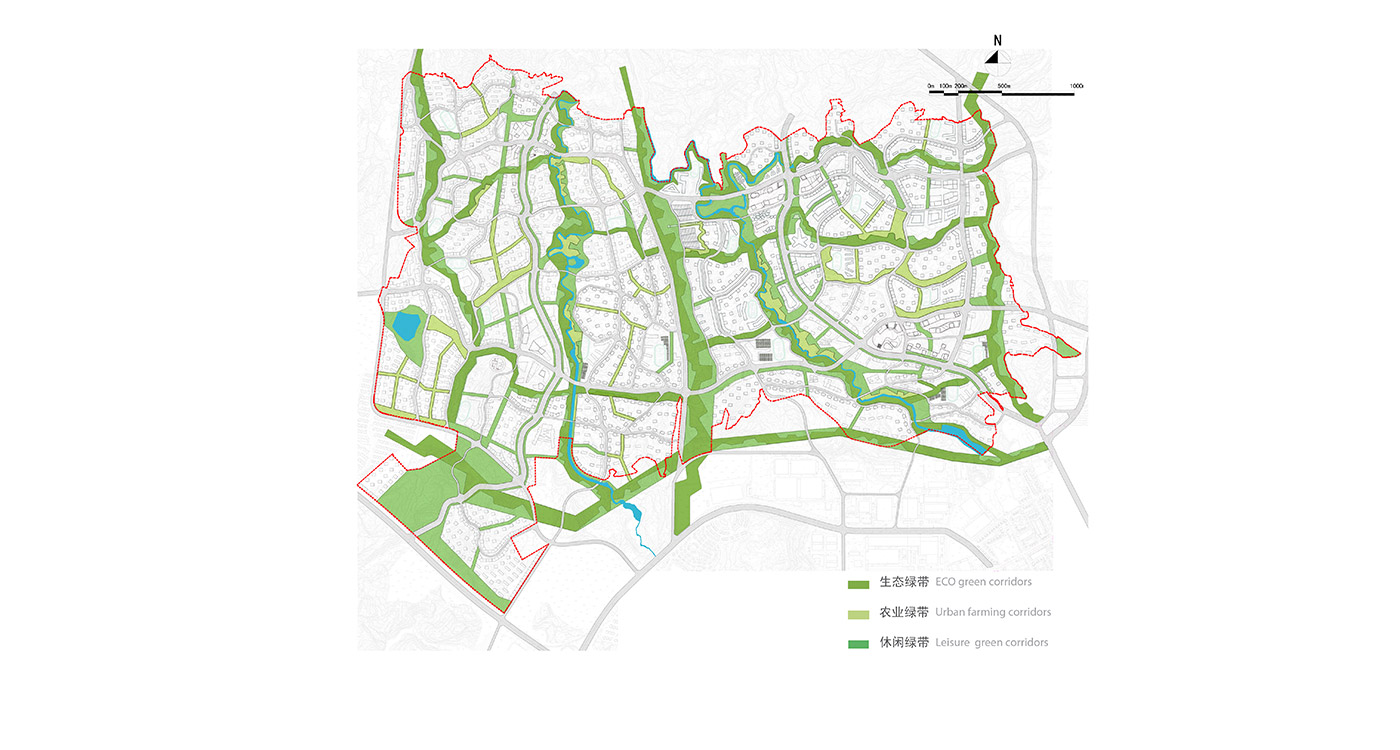
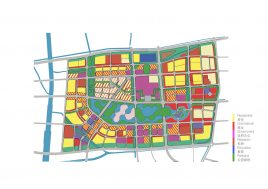
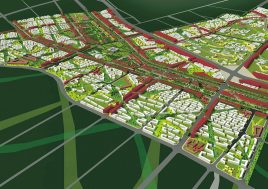
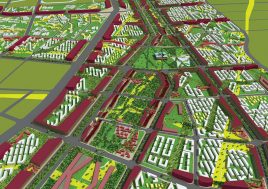
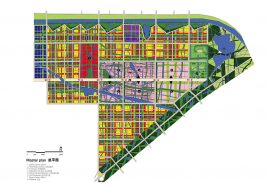
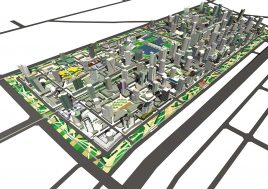
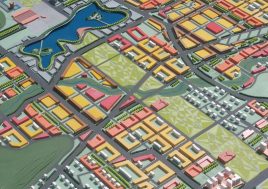
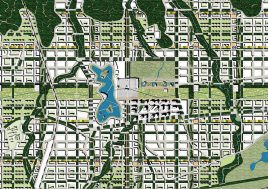
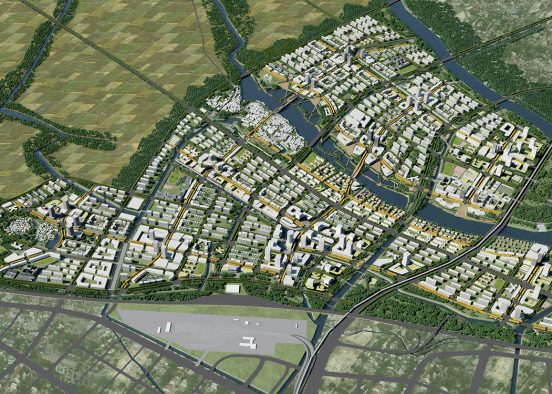
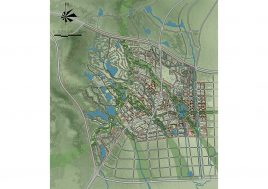
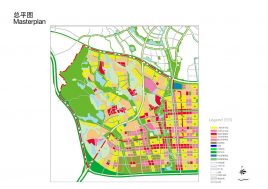
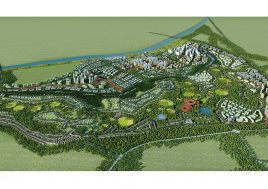
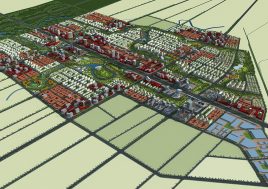
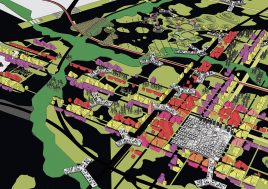
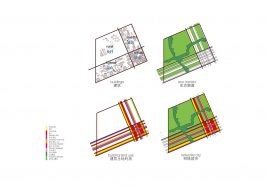
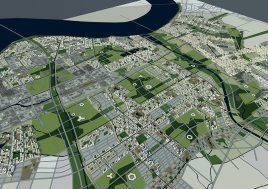
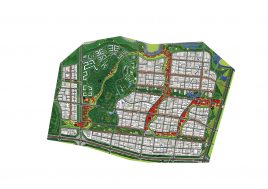
BAU’s urban design structure emerges from the site’s topography, hydrology, and wind direction. A park network and eco corridors are situated in both the valleys and along the ridges of the N-S oriented mountain range. Road morphology is likewise structured along NS contour lines. Two light rail lines anchor the public transport at four stations.
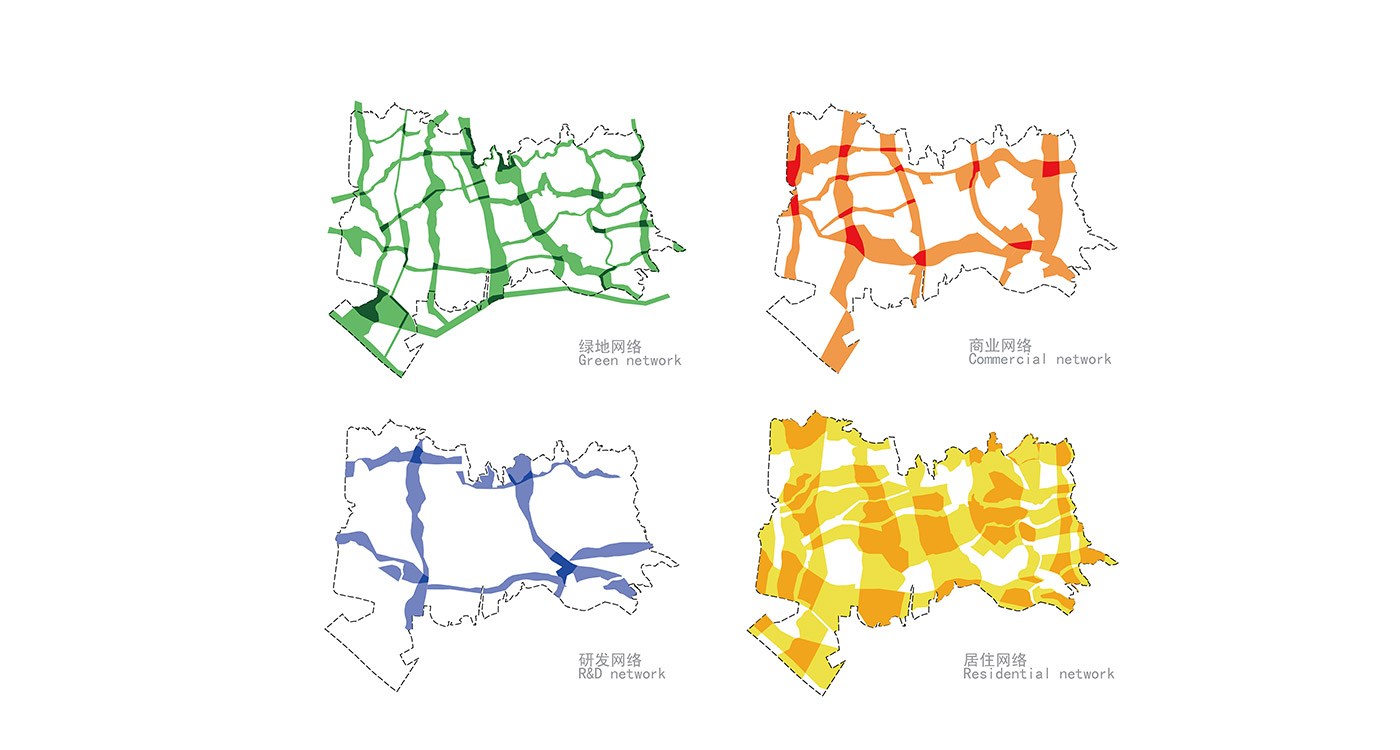
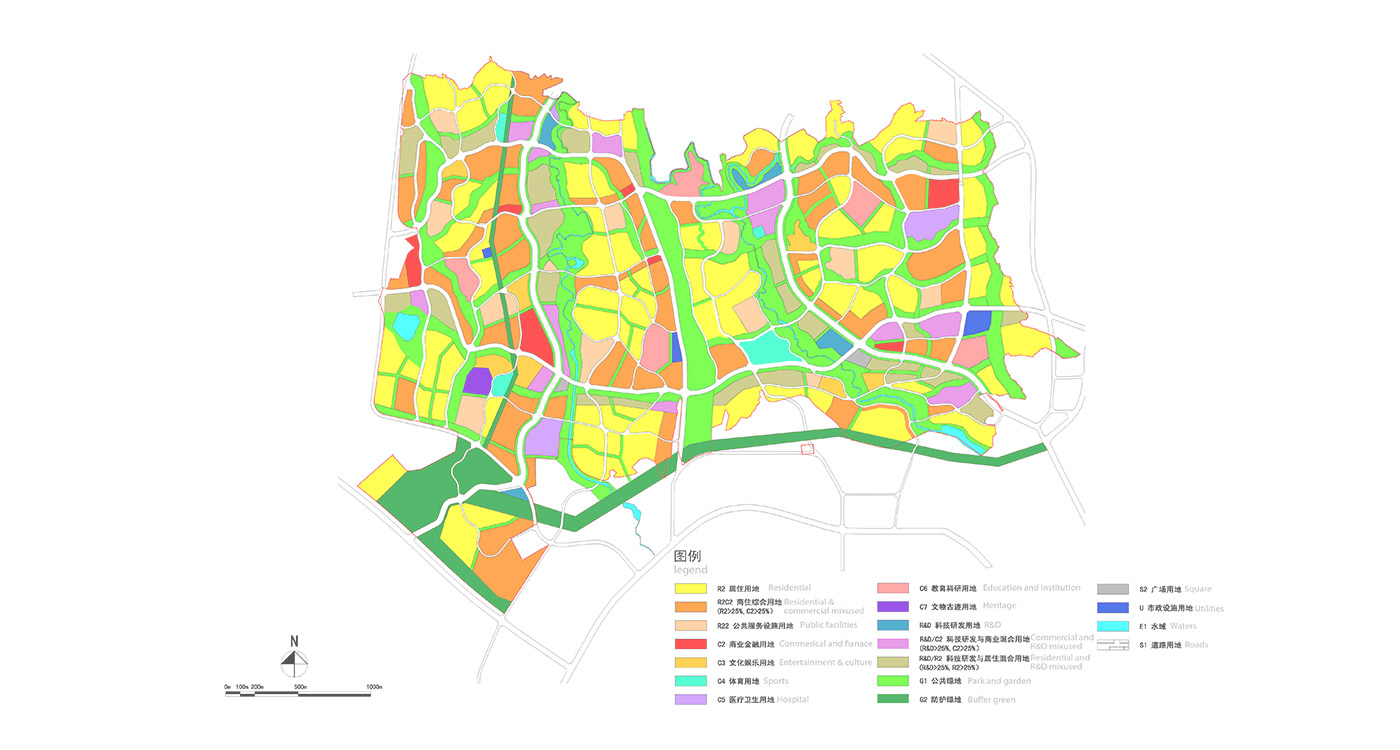
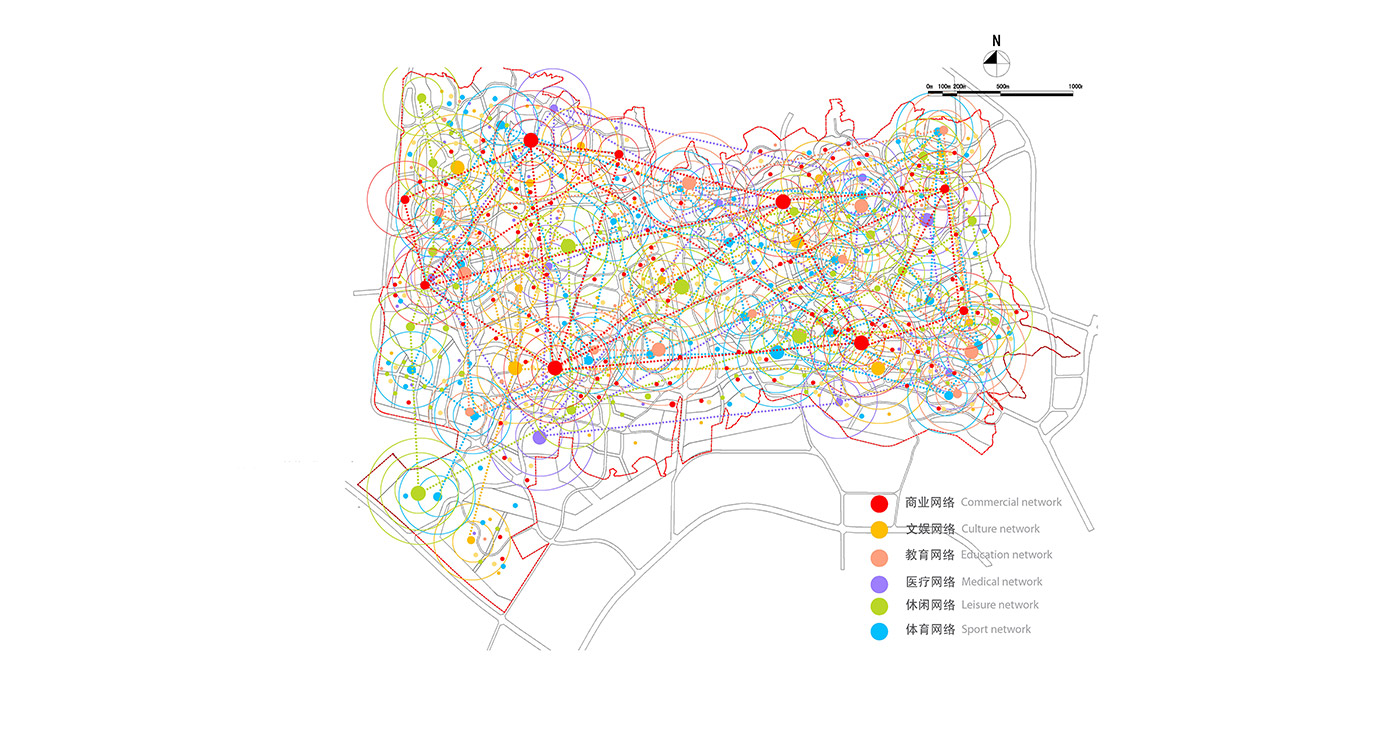
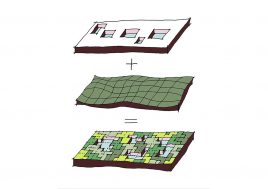
Land use is organized using a networks zoning strategy. It not only provides a degree of certainty for the city but also guarantees diversity and encourages complexity. Importantly the networks system provides a number of hybrid zones which enables the city a high degree of flexibility to adopt more of one use than another, and enables it to change over time without having to rezone the city’s planning scheme.
business segmentation
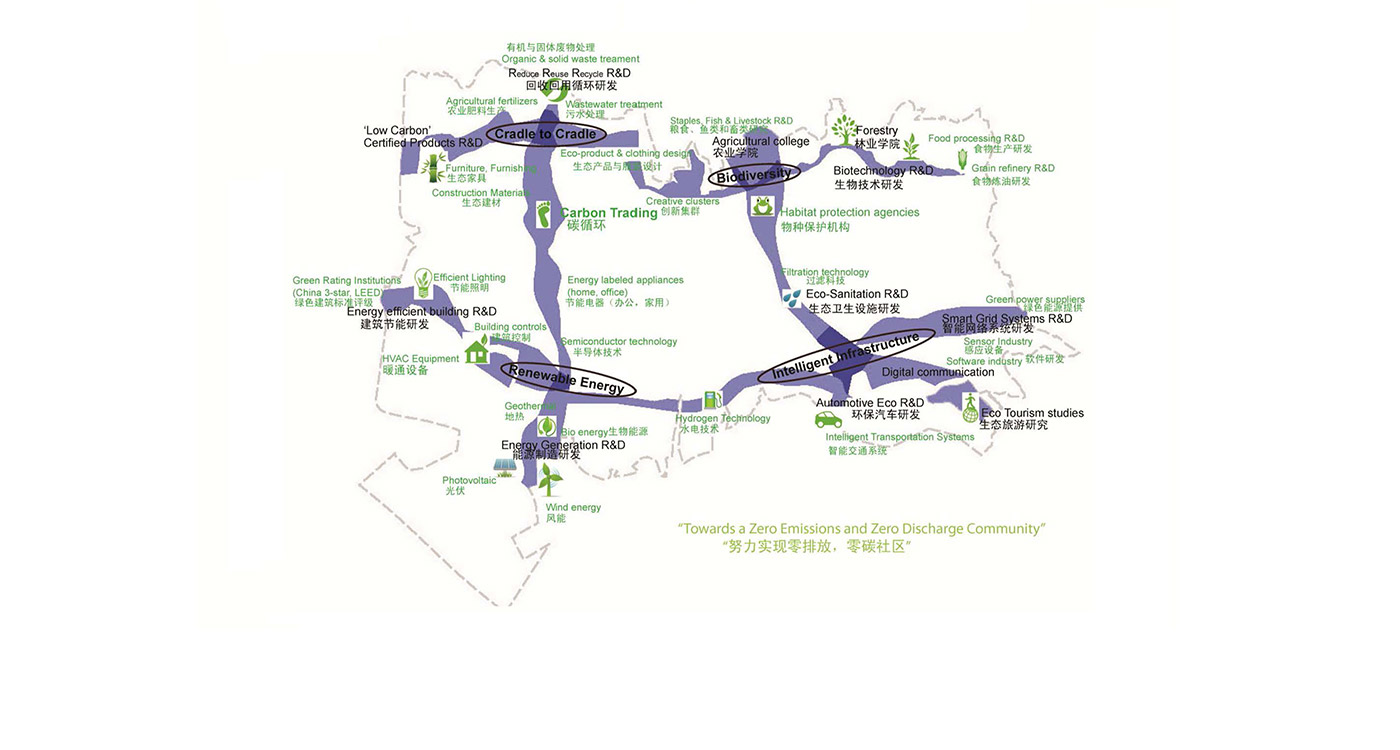
This proposal goes beyond the competition brief for a residential suburb. It proposes that the new district be a mix of living and working. In order to attract businesses we propose an industry theme unlike any other in Chongqing. This theme is not a standard segmentation, ie by types of industry, but is a segmentation based on an activity carried out within the entire spectrum of industries: research and development in ecologically sustainability.
There is little doubt that throughout the next four decades each and every industry will devote increasing capital into making their products or services more environmentally sustainable. The Eco Valley Sustainable R&D theme proposal is based on the assumption that many businesses would benefit from locating their Eco R&D in a location specializing in such research, and where the city is in fact an example in best practice of sustainable urbanism. Businesses would find their mission easier to fulfill in a district where they are surrounded by others in similar pursuit. Exchange of ideas, and business networking can bring about constructive cross fertilization. Appropriate staff would be attracted to such an eco work environment, as well as by the sustainable city itself.
creative culture
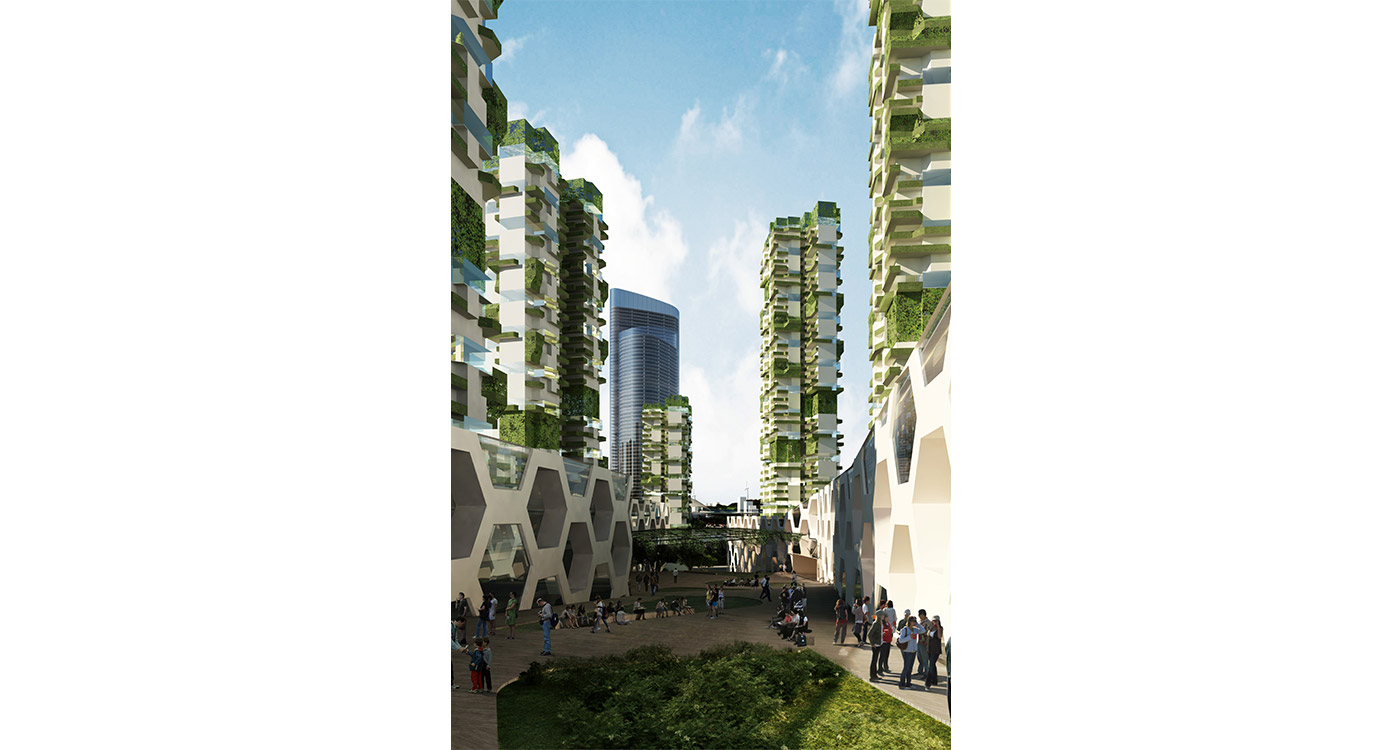
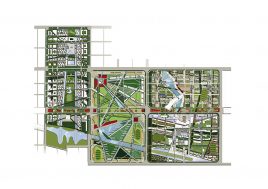
R&D is creative by definition. The most successful creative cities support what has been coined “the creative class”. It is well documented that such a creative class seek places of tolerance and places where there is a complex urban mix of activity and diverse subcultures. China’s new mono-functional districts of large scale projects are not conducive to the emergence of complex urbanity. Eco Valley applies a new model in order to provide maximum potential for the emergence of culture and community. The Eco Valley R&D zone is not an isolated office park zone; by utilizing our Networks Cities strategy the R&D can benefit from adjacency to many other city land-uses and programs (see section on networks cities).
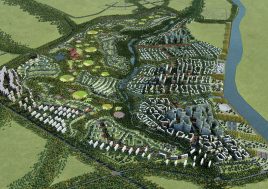
landmark district
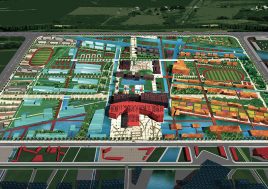
To reinforce the city’s image as a unique place of Eco R&D, a number of landmark nodes are planned. These nodes are where universities team together with private enterprise in purpose built facilities. Lecture and exhibition facilities provide the broader public with the opportunity to learn of the many aspects of sustainability. The four sub-centers of the district are given sub-themes of Eco R&D: Cradle to cradle; intelligent infrastructure; renewable energy; and bio-diversity.
eco valley adopts a new form of self-sufficient urbanism
biodiversity
Connected eco corridors with urban farming, recreational green, and protected green areas
– Long term management plan to conserve existing or create new on-site native habitats, water bodies, wetlands and their buffers.
– Community based (community garden) food production to support local economic value. Green roofs and green streets with bioswales and infiltration ditches
– Landscape and vegetation areas are largely self-sufficient by locally adapted plants & require little irrigation
energy
Certified Green Building:
– Every New Construction is China 3-star rated (Ministry of Housing and Urban Rural Development) and reduces the energy demand by 65% compared to 1980 benchmark.
Heat Island control:
– Average daily outdoor heat island intensity for built-up areas is not higher than 1.5°C.
– Wind corridors for efficient heat dissipation from built-up areas
– Tree lined and shaded streets, green roofs or cool roofs (high SRI) for enhanced microclimate
Onsite renewable energy sources:
– Major potential by Biomass energy and Surface Geothermal energy,
– Minor potential by Low Speed Urban Wind turbines, and PVT-solar concentrators
Combined Heat and Power (CHP) District system:
– Proximately 80% of the district’s heating and cooling consumption is provided by the district plant
Infrastructure Energy efficiency:
– Smart electricity grid to balance peak power demands.
water
Ecological Sanitation System
– Reduced dependency on municipal water supply
– Preference for modular and cost-efficient solutions based on decentralised partial-flow systems
– Conservation of resources by safe and hygienic recovery and reuse of nutrients and organics in the water
– Improvement of health by minimising the introduction of pathogens from human excreta into the water cycle
Onsite Waste-Water Treatment
– Treatment of blackwater to recycle water in drinking quality by Small Footprint MBR (Memb. Bio Reactor)
Sustainable Urban Drainage System
– Comprehensive stormwater management plan that retains on site minimum 80% of rainfall trough infiltration, evapotranspiration or reuse
waste
Recycling or reuse stations
– On every block or at least every 250m, containers for: paper, cardboard, glass, plastics, metal
Valley central utility corridor connected to Eco-tech recycling facility.
– Cleaner environment and get garbage vehicles off the road.
– Onsite processing of organic waste into energy and fertilizers, which are used for local urban farming
Recycling and salvage of 50% nonhazardous construction and demolition debris

































































































































































































































































































































 Back to projects
Back to projects